Frequency Distribution in Statistics Pdf
Introduction to Statistics and Frequency Distributions. Frequency Distributions and Descriptive Statistics in SPSS In this tutorial were going to work through a sample problem and construct frequency distributions and view some basic descriptive statistics.
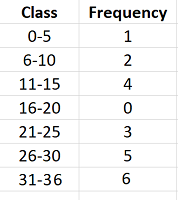
Cumulative Frequency Distribution Simple Definition Easy Steps
The class width is the distance between lower or upper limits of consecutive classes.

. A record of frequency or number of individuals in each category. We will then generate a histogram based on the results. 2 Find the value of the range.
Males Cumulative Scores less than 40 1 less than 50 4 less than 60 9. A frequency polygon aids in the easy comparison of two frequency distributions. What is Frequency Distribution Table and How to Make it.
The class width is 4. Males Relative Scores 30 - 39 24 40 - 49 71 50 - 59 119 60 - 69 214 70 - 79 143 80 - 89 238 90 - 99 190 Cumulative Frequency Distribution. Of orders received each day during the past 50 days at the office of a mail-order.
Picturing the World 3e 5. Stem-and-leaf plot stemplot is an excellent way to begin an analysis. Most students benefit from a few repetitions.
29 34 54 36 27 44 54 32 46 33 23 33 67 22 44 55 33 67 87 41 Construct a frequency. Thus 2550100 50 and 25100100 25. The set of categories that make up the original measurement scale.
A frequency table is a list of possible values and their frequencies. Grade 9 Introduction to Statistics Page 1 STATISTICS 1 MODULE 20 DISPLAYING QUALITATIVE VARIABLES Lesson 21 Frequency and Relative Frequency Distributions Time Limit 30 minutes TARGET At the end of this lesson the learner is expected to. By converting frequencies to relative frequencies in this way we can more easily compare frequency distributions based on different totals.
Since our data is. 121 Sampling Frequency Distributions and Graphs Probability and Cumulative Distribution Functions Another Example Suppose the cumulative distribution function for the height of Lesson2021ppt Free PPT in Biostatistics Statistics. We use an X as the column heading.
1 Find the highest and lowest value. That is rf f n 100 The ages of 100 residents of City A. The number of hours taken by transmission mechanics to remove repair and replace transmissions in one of the Transmission Fix-It stores one day last week are recorded as follows.
They are listed in a column from highest to lowest. A bar chart consists of bars corresponding to each of the possible values whose heights are equal to the frequencies. 5 1 4 9 5 4 13 9 4 17 13 4 The range is the difference between the maximum and minimum data entries.
To construct a stemplot start by drawing the stem. Frequency Table or Frequency Distribution Example. And construct a frequency distribution table using technology.
Should complete all of the practice problems. Larson Farber Elementary Statistics. A frequency polygon illustrating the data in.
To turn a raw frequency into a relative frequency divide the raw frequency by the total number of cases and then multiply by 100. RELATIVE FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION TABLE A relative frequency distribution indicates how many percent fall within each category. Lowest highest r 3 Decide the number of classes k to use between 5 and 15 4 Find the suggested class width.
Statistics are used to make decisions and predict what may happen in the future. The following are the steps of constructing a grouped frequency distribution. A frequency distribution is a table in which measurements are tallied and the frequency or total number of times that each item.
A frequency distribution is an organized tabulation of the number of individuals located in each category on the scale of measurement. Frequency Distributions and Graphs Santorico -Page 27 Section 2-1 Organizing Data Data must be organized in a meaningful way so that we can use it effectively. Stem-and-Leaf Plots Stemplots The.
1 Find the minimum and the maximum value. X is the midpoint of the class. Frequency distribution is a table that displays the frequency of various outcomes in a sample.
The relative frequencies are obtained by simply dividing the class frequencies by n and then multiplying by 100. Before constructing a frequency table one. Each entry in the table contains the frequency or count of the occurrences of values within a particular group or interval and in this way the table summarizes the distribution of values in the sample.
A frequency distribution table shows the different. Note that we lose some information from our original data set by separating the data Eye Color of Students Category Frequency Blue 4 Brown 6 Gray 2 Hazel 5 Green 3 Total 20 Pets of Students. Frequency distribution the organization of raw data in table form using classes and frequencies.
If you display data. The following table gives the frequency distribution of the number. Collecting and organizing data Data that have been collected but not organized in any way are called raw data.
Ten men and ten women participated in a threepoint shootout. When the total frequency is large and the class intervals are narrow the frequency polygon becomes a smooth curve known as the frequency curve. This is often a pre-cursor to creating a graph.
Frequency Distributions Groups of data have little value until they have been placed in some kind of order. Example The numbers of accidents experienced by 80 machinists in a certain industry over a. Data Set 1 Here are frequency distributions for the data on eye color and number of pets owned.
Up to 24 cash back Frequency Distribution Worksheet. It is adding the class limits and divide by 2. Such a group is an array or distribution.
Measurement categories and the number of observations in. Finally use the activities and the practice problems to study. A frequency distribution presents an organized picture of the entire set of scores and it shows where each individual is located relative to others in the distribution.
Should have an idea. Sorted displayed and analyzed. Identify the necessary information for a frequency distribution table.
Raw data are difficult to interpret so it can be arranged in a frequency table. Stem-values represent either the first or first-two. The set of categories that make up the original measurement scale.
It has two elements. Consider this small data set. Elementary Statistics Making Frequency Table Objective.
FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION A frequency distribution can be structured either a graph or a table. The additional practice helps consolidate what you have learned so you dont forget it during tests. Usually measurements are arranged in ascending or descending order.
A frequency distribution can be structured either as a table or as a graph but in either case the distribution presents the same two elements. Of each problem type. 218 426 53 116 309 504 281 270 246 523.
2 Find the range. A frequency distribution is an organized tabulation showing exactly how many individuals are located in each category on the scale of measurement. Statistics for Engineers 4-2 The frequency of a value is the number of observations taking that value.
3 Find the class width if we wish to have a frequency distribution table with 5 classes.

Lesson 5 Frequency Distribution Table In Statistics Youtube
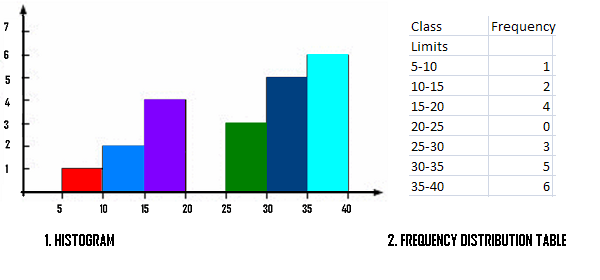
Cumulative Frequency Distribution Simple Definition Easy Steps

How To Calculate A Frequency Distribution Table Second Example Youtube
No comments for "Frequency Distribution in Statistics Pdf"
Post a Comment